
International business correspondent
 BBC
BBCListen to Theo read this article
“What you have there is about £250,000 worth of gold,” Emma Siebenborn says as she shows me a faded plastic tub filled with old, shabby jewellery – rings, charm bracelets, necklaces and orphaned earrings.
Emma is the strategies director of Hatton Garden Metals, a family-run gold dealership in London’s Hatton Garden jewellery district, and this unprepossessing tub of bric-a-brac is a small sample of what they buy over the counter each day. It is, in effect, gold scrap, which will be melted down and recycled.
Also on the table, rather more elegantly presented in a suede-lined tray, is a selection of gold coins and bars. The largest bar is about the size and thickness of a mobile phone. It weighs a hefty 1kg, and it’s worth about £80,000.
The coins include biscuit-sized Britannias, each containing precisely one ounce of 24 carat bullion, as well as smaller Sovereigns. These are all available to buy – and the recent surge in gold prices has led to a surge in demand.
Zoe Lyons, who is Emma’s sister and the managing director, has never seen anything like it – often she finds would-be sellers queuing in the street. “There’s excitement and buzz in the market but also nervousness and trepidation,” she tells me.
“There’s anxiety about which way the market is going to go next, and when you get those emotions, ultimately it creates quite big trades.”
At MNR jewellers a couple of streets away, a salesman agrees: “Demand for gold has increased, definitely,” he says.
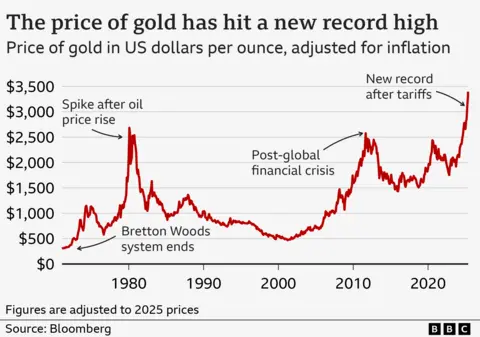
Gold is certainly on a roll. Its price has increased by more than 40% over the past year. In late April it rose above $3,500 (£2,630) per troy ounce (a measurement for precious metals). This marked an all-time record, even allowing for inflation, exceeding the previous peak reached in January 1980. Back then the dollar price was $850, or $3,493 in today’s money.
Economists have attributed this to a variety of factors. Principal among them has been the unpredictable changes in US trade policy, introduced by the Trump administration, the effects of which have shaken the markets. Gold, by contrast, is seen by many as a solid investment. Fears about geopolitical uncertainty have only added to its allure. Many investors have come to appreciate the relative stability offered by a commodity once dismissed by the billionaire Warren Buffett as “lifeless” and “neither of much use nor procreative”.
“It’s the kind of conditions that we consider a bit of a perfect storm for gold,” explains Louise Street, senior markets analyst at the World Gold Council, a trade association funded by the mining industry.
“It’s the focus on potential inflationary pressures. Recessionary risks are rising, you’ve seen the IMF [International Monetary Fund] downgrading economic forecasts very recently…”
But what goes up can also come down. While gold has a reputation as a stable asset, it is not immune to price fluctuations. In fact, in the past,…
Read More: Gold is booming – but how safe is it for investors, really?




